Elbow
Biceps Tendon Tear at the Elbow
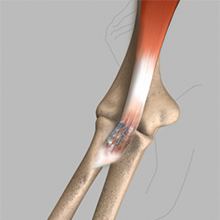
The biceps muscle, located in the front of the upper arm allows you to bend the elbow and rotate the arm. Biceps tendons attach the biceps muscle to the bones in the shoulder and in the elbow.
Biceps tear can be complete or partial. Partial biceps tendon tears will not completely break the tendon. Complete tendon tears will break the tendon into two parts.
Distal Biceps Rupture
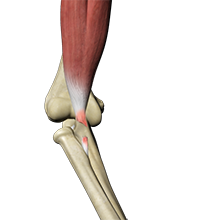
The biceps muscle is located in front of your upper arm. It helps in bending your elbow as well as in rotational movements of your forearm. Also, it helps to maintain stability in the shoulder joint. The biceps muscle has two tendons, one of which attaches it to the bone in the shoulder and the other attaches at the elbow. The biceps tendon at the elbow is called the distal biceps tendon and if there is a tear in this tendon, you will be unable to move your arm from the palm-down to palm-up position.
Elbow Dislocation
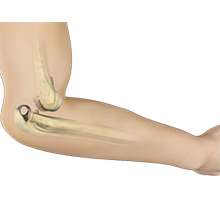
The elbow is a hinge joint made up of 3 bones – humerus, radius and ulna. The bones are held together by ligaments to provide stability to the joint. Muscles and tendons move the bones around each other and help in performing various activities. Elbow dislocation occurs when the bones that make up the joint are forced out of alignment.
Elbow Injuries in the Throwing Athlete
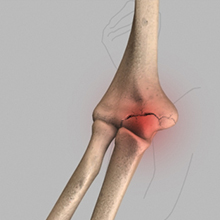
An athlete uses an overhand throw to achieve greater speed and distance. Repeated throwing in sports such as baseball and basketball can place a lot of stress on the joints of the arm, and lead to weakening and ultimately, injury to the structures in the elbow
Elbow (Olecranon) Bursitis
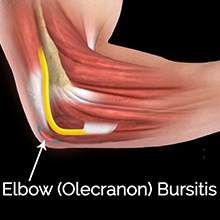
The elbow contains a large, curved, pointy bone at the back called the olecranon, which is covered by the olecranon bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that allows smooth movement between the bone and overlying skin. Inflammation of this bursa leads to a condition called olecranon bursitis.
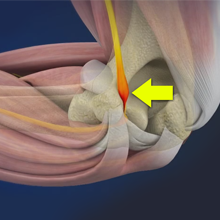
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans is a joint condition in which a piece of cartilage, along with a thin layer of the bone separates from the end of the bone because of inadequate blood supply. The separated fragments are sometimes called “joint mice”. These fragments may be localized, or may detach and fall into the joint space causing pain and joint instability.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a condition characterized by compression of the ulnar nerve in an area of the elbow called the cubital tunnel.
The ulnar nerve travels down the back of the elbow behind the bony bump called the medial epicondyle, and through a passageway called the cubital tunnel.
Tennis Elbow
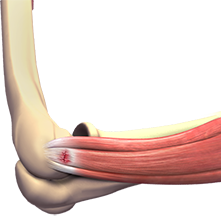
Tennis elbow is the common name used for the elbow condition called lateral epicondylitis. It is an overuse injury that causes inflammation of the tendons that attach to the bony prominence on the outside of the elbow (lateral epicondyle).It is a painful condition occurring from repeated muscle contractions at the forearm that leads to inflammation and micro tears in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle.
Golfer’s Elbow
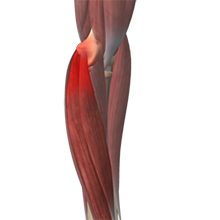
Golfer’s elbow, also called Medial Epicondylitis, is a painful condition occurring from repeated muscle contractions in the forearm that leads to inflammation and microtears in the tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle.
Adult Forearm Fractures
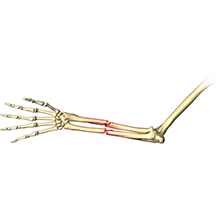
The forearm is made up of 2 bones namely the radius and ulna. The primary function of your forearm is rotation i.e., the ability to turn your palms up and down. The fracture of the forearm affects the ability to rotate your arm, as well as bend and straighten the wrist and elbow.
Forearm Fractures in Children
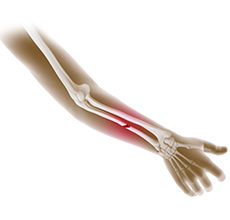
The radius (bone on the thumb side) and ulna (bone on the little-finger side) are the two bones of the forearm. Forearm fractures can occur near the wrist, near the elbow or in the middle of the forearm. Apart from this, the bones in children are prone to a unique injury known as a growth plate fracture.
Distal Humerus Fractures of the Elbow
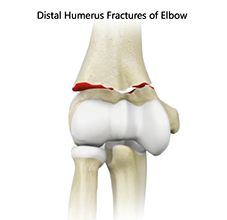
The elbow is a region between the upper arm and the fore arm. The elbow joint is made up of 3 bones. The distal (lower) end of the humerus bone in the upper arm joins with the radius and ulna bones in the fore arm to form the elbow joint.
Elbow Fractures
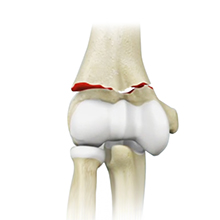
Three bones, the humerus, radius and ulna, make up the elbow joint. Elbow fractures may occur from trauma, resulting from various reasons; some of them being a fall on an outstretched arm, a direct blow to the elbow, or an abnormal twist to the joint beyond its functional limit.
Biceps Tendon Repair
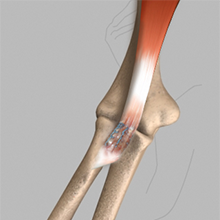
The biceps muscle is located in front of your upper arm. It helps in bending your elbow as well as in rotational movements of your forearm. Also, it helps to maintain stability in the shoulder joint. The biceps muscle has two tendons, one of which attaches it to the bone in the shoulder and the other attaches at the elbow.
Elbow Arthroscopy
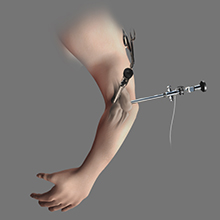
Elbow arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is performed through tiny incisions to evaluate and treat several elbow conditions.
The Elbow is a complex hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones - humerus, radius and ulna.
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Reconstruction
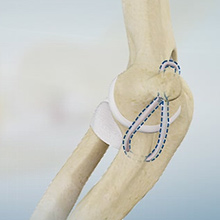
The elbow is a complex joint of the upper limb formed by the articulation of the long bone of the upper arm or humerus and the two bones of the forearm, namely, radius and ulna. It is one of the important joints of the upper limb and is involved in basic movements such as flexion and extension of the upper limb and rotation of the forearm.
Ulnar Nerve Subluxation
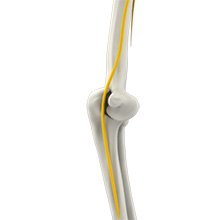
Ulnar nerve subluxation is a condition in which pain and a snapping is felt on the inside of the elbow when the arm is flexed and extended. This happens as the ulnar nerve dislocates and then relocates in relation to the medial epicondyle (bony projection on the inside of the elbow). Numbness and tingling may be present and radiates to the fingers. Ulnar nerve subluxation is usually treated by conservative measures. Surgery may be recommended for severe symptoms.







